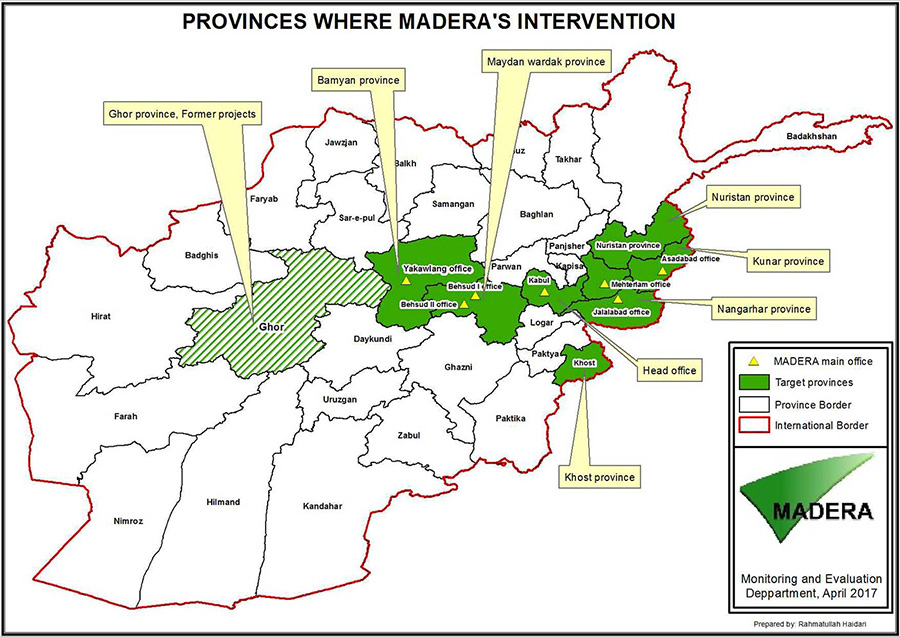
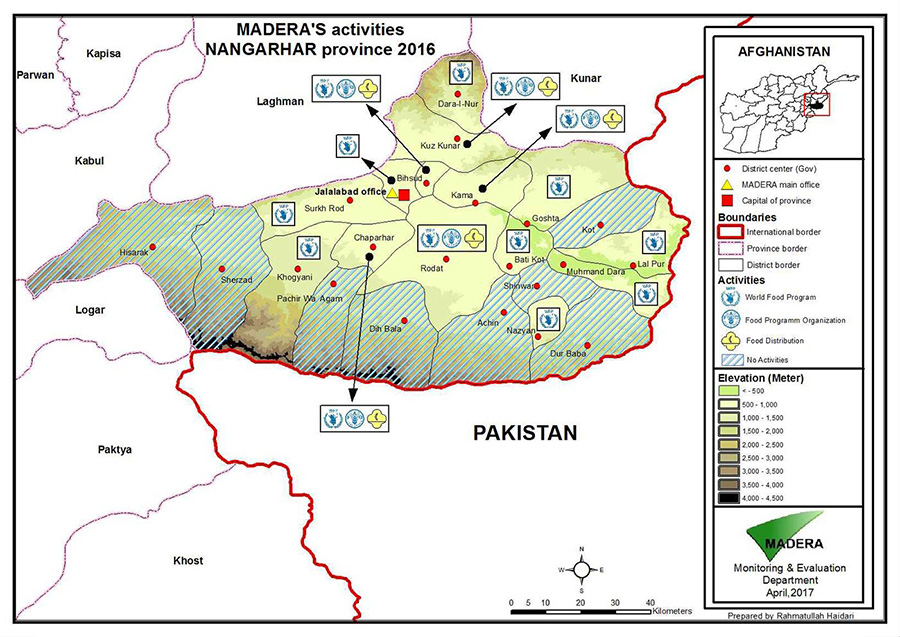
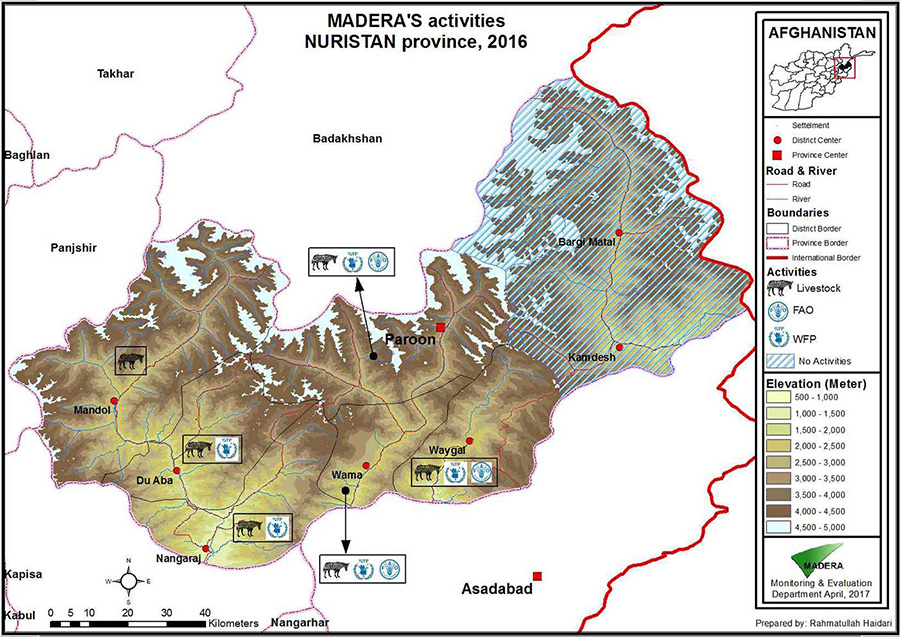
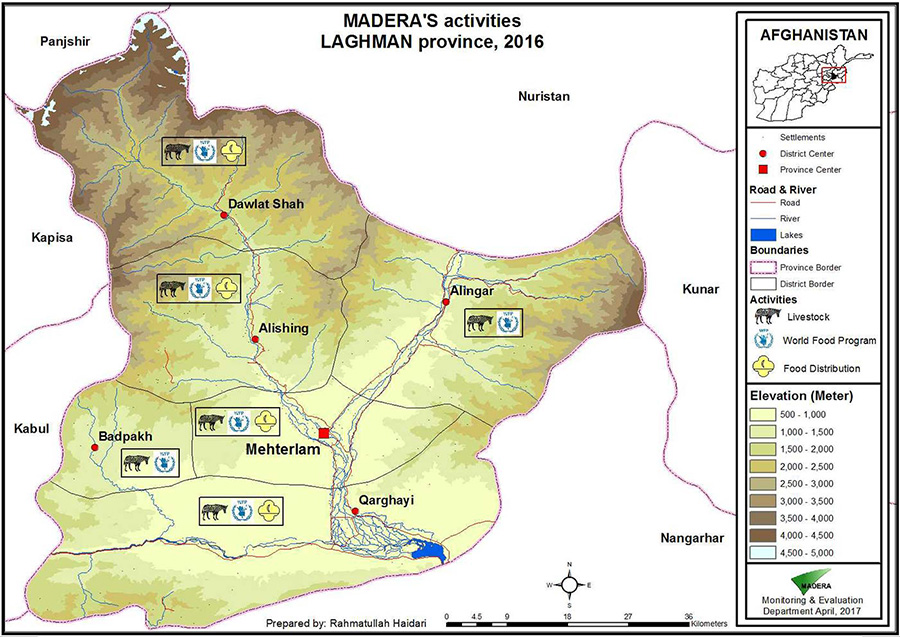
Our Areas of intervention
History of activities in the Eastern region
As soon as 1985, the BIA and then MADERA intervene in the high valleys of Kunar, Nuristan and Laghman. In the context of war led by the Soviet army, the association first implemented agropastoral and cereal programs, as well as forest preservation actions, to support rural communities and avoid their exile to Pakistan. Gradually, activities spread to the lower valleys and aimed at helping refugees return, after the withdrawal of the Soviets.
From 1992, the programs diversify and include the re-cultivation of lands left undeveloped during the war, the distribution of adapted seeds, the rehabilitation of irrigation systems, the vaccination of herds, the creation of fruit and forest nurseries.
In 1997, a laboratory for the diagnosis of animal diseases and manufacture of animal vaccines was created by MADERA in Jalalabad. It covers eastern Afghanistan.
In 2002, to cope with the massive return of refugees to Afghanistan, a major program of creation of arable land through the extension of irrigation networks was implemented. Actions in the field of livestock farming, agriculture, arboriculture and micro-credit complemented it and forestry activities continued in parallel in the high valleys of Kunar and Nuristan. In addition, several participatory community development pilot projects started: creation of protection dikes, well drilling, eucalyptus plantation.
From 2004 to 2017, MADERA is one of the facilitators of the National Solidarity Program (NSP), which allows village communities, represented by elected committees, to implement development projects on their own.
In April 2007, a sustainable horticulture program was launched, aimed at helping fruit producers organize marketing channels.
In October 2008, a new community development project is initiated in parallel to the National Solidarity Program (NSP), which consists in defining a district-level (and not the village anymore) development plan that meets the needs of all the concerned villages.
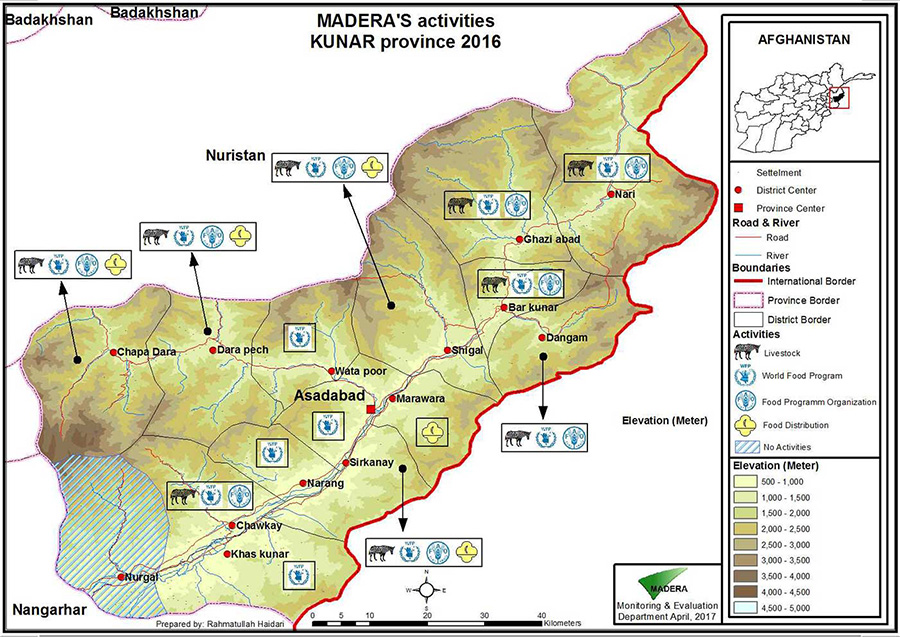
Currently, MADERA works in this region on animal health and animal husbandry programs (setting up a network of veterinarians and para-veterinarians, and vaccination campaigns), arboriculture and forest protection (sustainable horticulture program and agroforestry) and civil engineering (support to infrastructure design and rehabilitation).
History of activities in the Central region (Hazarajat)
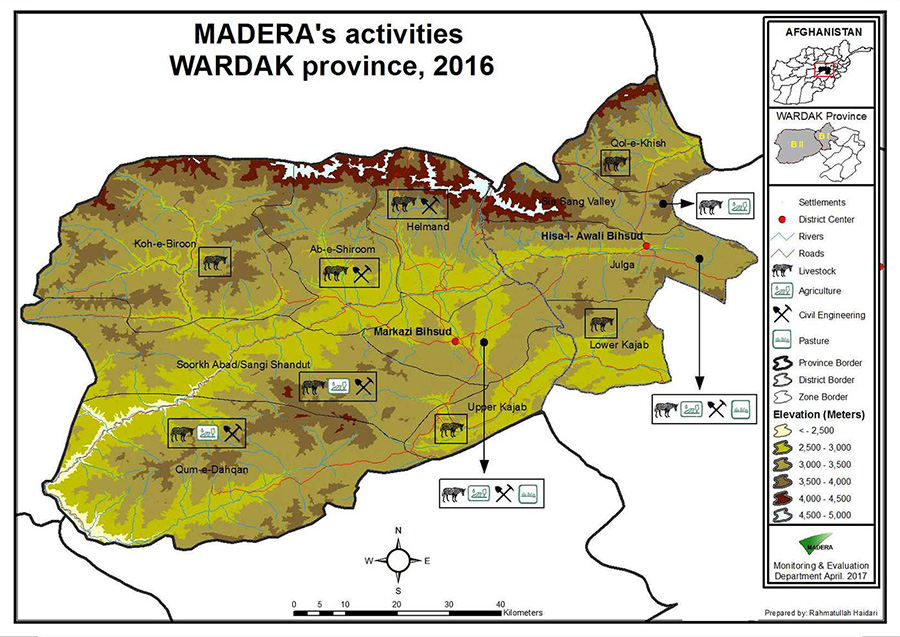
Since 1992, MADERA has been running rural development programs in Wardak Province, specifically in Behsud 1 and 2 districts.
The first actions involved the introduction of market gardening and new vegetable varieties to diversify the diet, and then research on cereal varieties adapted to the region in cooperation with other NGOs and FAO.
From 1998, animal vaccination campaigns are conducted, in parallel with the setting up of a network of para-veterinarians for animal health.
In 2001, fruit tree and poplar cultivation programs began, with the aim of increasing and diversifying farmers' incomes (selling poplars and fruits in Kabul).
Support for local craftsmanship is addressed in 1999 with the introduction and learning of the spinning technique.
More recently, the construction of hydraulic micro-plants and bioclimatic greenhouses has been encouraged and supported by our teams. These development activities have often included in parallel emergency operations such as distributions of "food against work", due to droughts and lack of food.
For several years, MADERA has been carrying out projects for the creation of road and the rehabilitation of runways. But also snow removal programs to open up the region during the winter months. More recently MADERA’s projects also tackled the rehabilitation and expansion of irrigation reservoirs to extend cultivable areas.
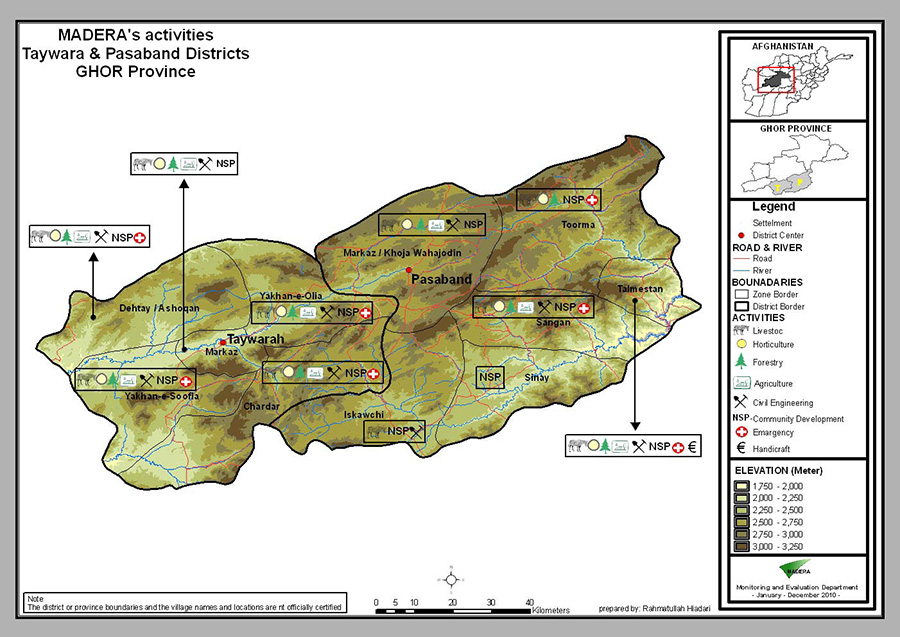
History of MADERA’s activities in Ghor
MADERA started in 2001 activities focused on rural rehabilitation and food security as well as emergency distribution actions in the 2 southern districts of the province (Taywarah and Passaband).
Thus over the period 2001-2002 MADERA carried out emergency programs of rehabilitation of roads and tracks remunerated in the form of "food for work".
In 2002, MADERA undertook a participatory survey of local populations to identify and prioritize their needs with their collaboration.
Between 2003 and 2006 MADERA conducts several programs including:
· construction and rehabilitation of tracks and roads;
· agriculture: variety testing, seed multiplication;
· arboriculture: creation of nurseries for the introduction of fruit species and timber;
· support for the creation of associations;
· school constructions;
· breeding: improvement of the diet (nutritious supply of minerals through the distribution of lick stones) and conditions of stabling;
· crafts: introduction of spinning wheels for wool.
Between 2007 and 2009 MADERA pursues and develops programs of fruit and non-fruit arboriculture, agriculture and zootechnics. Then MADERA started community development programs within the framework of the "national solidarity program" working with 80 villages.
Finally, MADERA provided one-off emergency assistance when droughts affecting the region.